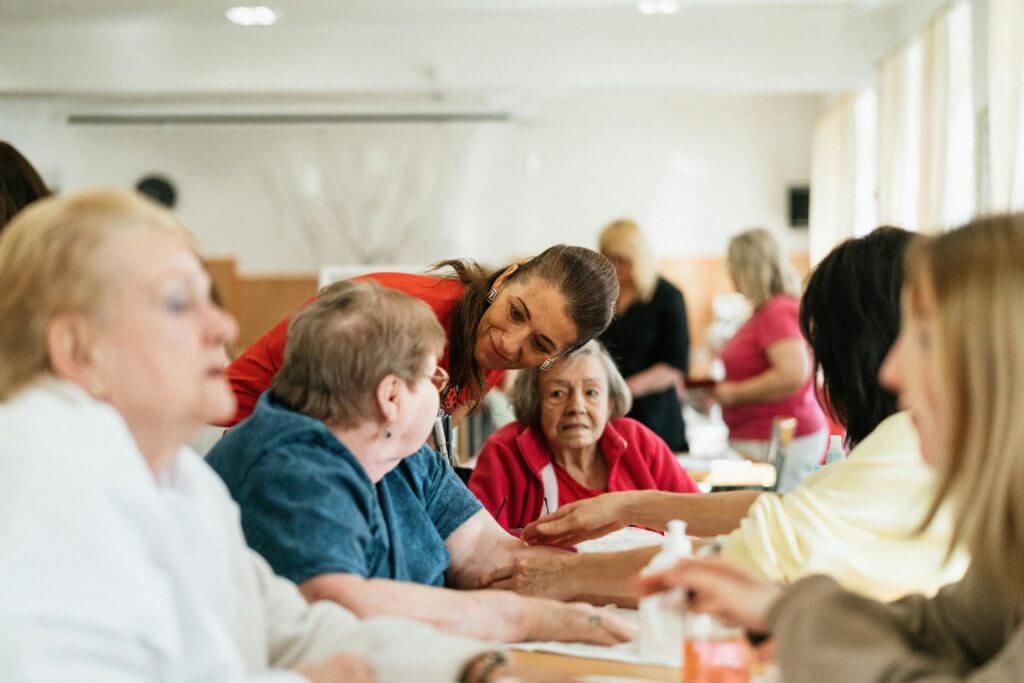
Dementia is a complex and progressive neurodegenerative condition that affects cognitive, functional, and behavioral abilities. Patients with dementia often experience a decline in their physical and cognitive functioning, leading to a reduced quality of life. Occupational therapy (OT) and physical therapy (PT) are two essential components of a comprehensive care plan for individuals with dementia. This report aims to provide an overview of the role of OT and PT in the management of dementia and highlight their significance in enhancing the well-being of patients.
Occupational therapy (OT) and physical therapy (PT) stand at the forefront of dementia care, offering vital interventions that address the multifaceted challenges faced by patients. These therapeutic approaches are instrumental in preserving and improving the physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being of individuals navigating the complex terrain of dementia. This guide sets the stage for an exploration of the pivotal roles that OT and PT play in the holistic care and management of dementia patients. While OT and PT each address specific facets of dementia care, they are most effective when integrated into a multidisciplinary care plan. Collaborative efforts among healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, psychologists, and social workers, are essential to provide comprehensive support to dementia patients. Furthermore, involving family members and caregivers in the therapeutic process is crucial for achieving the best outcomes and maintaining continuity of care.
Occupational Therapy for Dementia Patients:
1. Functional Independence
Occupational therapists work to enhance the functional independence of dementia patients. They assess the patient’s abilities and design interventions to help them perform daily tasks such as dressing, grooming, and eating independently for as long as possible.
2. Cognitive Stimulation
OT includes cognitive stimulation activities that help maintain cognitive function. These activities involve memory exercises, problem-solving tasks, and engagement in
meaningful activities to promote mental well-being.
3. Behavioral Management
Occupational therapists also assist in managing challenging behaviors commonly associated with dementia, such as agitation and aggression. They develop strategies to reduce stress and improve the patient’s quality of life.
4. Environment Adaptations
OTs evaluate the patient’s living environment and make necessary modifications to ensure safety and accessibility. This may involve removing hazards, adding handrails, or simplifying the layout of the home.
5. Sensory Interventions
Sensory stimulation through activities like art, music, or aromatherapy can provide emotional comfort and improve the mood of dementia patients. Occupational therapists incorporate these activities into their treatment plans.
Physical Therapy for Dementia Patients:
1. Mobility Enhancement
Physical therapists focus on maintaining and improving the physical function of dementia patients. They design exercises and interventions to address issues such as muscle weakness, balance problems, and gait disturbances, which can enhance mobility.
2. Fall Prevention
Falls are a significant concern for dementia patients. PT interventions help reduce the risk of falls by improving balance and strength. Therapists may also recommend assistive devices like canes or walkers.
3. Pain Management
Patients with dementia may experience pain due to musculoskeletal conditions or other health issues. Physical therapists assess and manage pain through techniques such as manual therapy and exercise.
4. Joint Health
PT can help prevent joint contractures and maintain joint range of motion, which can be compromised in dementia patients who are less active.
5. Cardiovascular Health
Maintaining cardiovascular fitness is crucial. Physical therapists may implement low-impact aerobic exercises to enhance heart health.
Occupational therapy and physical therapy are integral components of dementia care that focus on improving the overall quality of life for patients. These therapies address a wide range of physical, cognitive, and behavioral challenges, enabling individuals with dementia to maintain their independence, manage their symptoms, and enhance their overall well-being. Collaboration between healthcare professionals, including occupational therapists, physical therapists, and other specialists, is essential to provide comprehensive care for individuals living with dementia.
Remember that every individual with dementia is unique, and their needs may change over time. Continuously assess the quality of care your loved one is receiving and be prepared to make adjustments as necessary to ensure their safety and happiness in a care community. We work on exercises and stretches that prevent falls before they happen. To learn more, call (904) 618-3778 or email seniorservicesfl@h2health.com.
For more resources, check out the Alzheimer’s Society.
To schedule an appointment or consultation, reach out to us.
Sources:
-
1. Alzheimer’s Association. (2021). Occupational Therapy and Dementia. [https://www.alz.org/media/Documents/occupational-therapy-dementia-ts.pdf]
2. American Physical Therapy Association. (2015). Physical Therapy Management of Individuals With Alzheimer Disease. [https://www.apta.org/Alzheimers/]