Dementia and Fall Prevention:
A Comprehensive Approach to Enhance Safety and Quality of Life
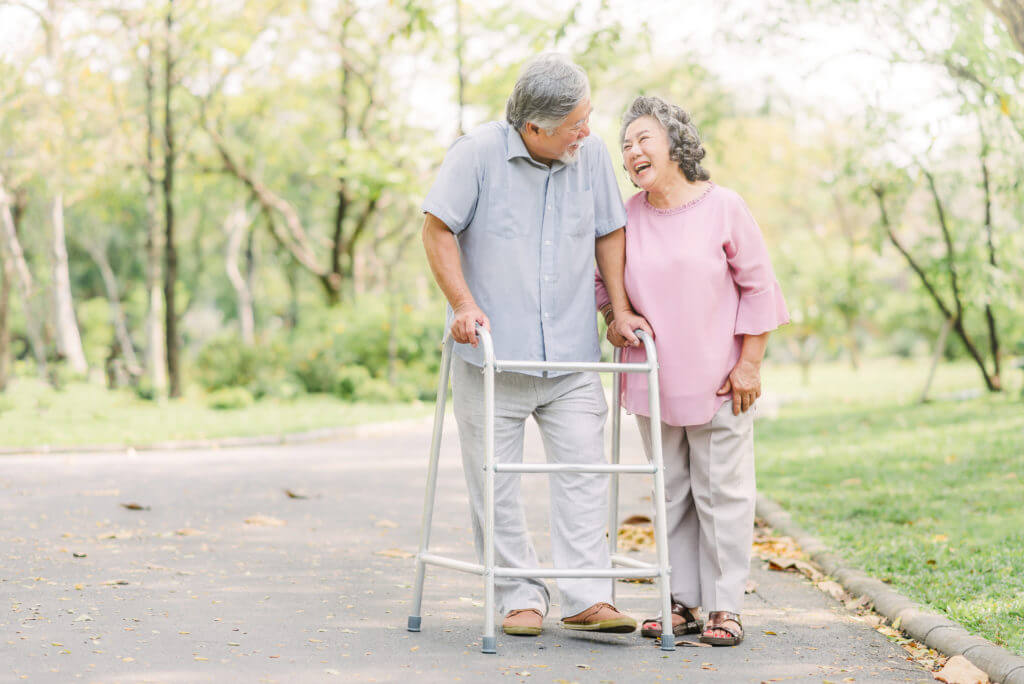
Dementia is a neurological disorder characterized by cognitive decline, memory loss, and impaired judgment. With an aging global population, the prevalence of dementia is on the rise, leading to increased concerns regarding the safety and well-being of affected individuals. One critical aspect of dementia care is fall prevention, given the heightened risk of falls in this vulnerable population. Fall prevention for people with dementia is crucial for patients with dementia as they are at a higher risk of experiencing falls due to impaired cognitive function and mobility issues. Implementing appropriate strategies can help reduce the risk of falls and improve their overall safety.
The Link between Dementia and Falls:
Research indicates that individuals with dementia have a two to three times higher risk of falling compared to older adults without cognitive impairment. The reasons for this increased risk include gait disturbances, balance issues, impaired spatial awareness, and decreased muscle strength. Additionally, dementia-related behavioral symptoms, such as wandering and agitation, can further contribute to falls. A multi-faceted approach is necessary to address the specific fall risk factors associated with dementia. This reference guide aims to provide caregivers, family members, and healthcare professionals with essential tips and strategies to prevent falls in patients with dementia. Falls can have severe consequences, but by implementing preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the risk and ensure their safety. The following strategies are effective in preventing falls in this population.
Ways to Prevent Falls & Enhance Safety
Fall prevention for people with dementia requires a multi-faceted approach that includes environmental modifications, regular exercise, and attentive supervision. By implementing these strategies and seeking professional guidance, we can significantly reduce the risk of falls and promote a safe and secure environment for individuals with dementia.
1. Conduct a Home Safety Assessment:
- Remove tripping hazards such as loose rugs, clutter, or electrical cords.
- Install adequate lighting throughout the living area, including nightlights in hallways and bathrooms.
- Secure handrails or grab bars in high-risk areas like staircases and bathrooms.
- Use nonslip mats or adhesive strips in the bathtub or shower to prevent slipping.
2. Promote Physical Activity and Exercise:
- Engage the individual in regular exercise to improve strength, balance, and coordination.
- Consult with healthcare professionals to develop a safe exercise plan tailored to the individual’s abilities.
- Encourage activities like walking, stretching, or gentle resistance exercises.
3. Assist with Mobility and Ambulation:
- Encourage the use of assistive devices such as canes, walkers, or wheelchairs as needed.
- Ensure assistive devices are properly fitted and regularly maintained.
- Provide clear pathways and remove obstacles that may impede safe movement.
- Offer support and supervision during walking or transferring to prevent falls.
4. Encourage Proper Footwear:
- Ensure the individual wears well-fitting, supportive footwear with nonslip soles.
- Discourage the use of high heels, loose-fitting slippers, or socks on slippery surfaces.
- Regularly check the condition of the individual’s shoes and replace them when necessary.
5. Supervise and Monitor Medication:
- Consult with healthcare professionals to review medications and potential side effects that may increase fall risk.
- Follow prescribed medication schedules and monitor for any adverse reactions.
- Be aware of medications that may cause dizziness or drowsiness and take necessary precautions.
6. Implement Visual Cues and Signage:
- Use clear and visible signs to indicate potential hazards, such as steps or wet floors.
- Label doors, cupboards, and drawers to aid in recognition and prevent confusion.
- Place contrasting colored tape or markings on steps or edges to enhance visibility.
7. Enhance Communication and Engagement:
- Maintain clear and open communication with the individual to understand their needs and concerns.
- Ensure eyeglasses and hearing aids are in good working condition to optimize sensory input.
- Engage the individual in meaningful activities and social interactions to promote mental and emotional well-being.
8. Utilize Physical and Occupational Therapy:
- Occupational Therapists will help with environmental modifications, changing activity patterns and behaviors, prescribe mobility aids, and help overcome the fear of falling.
- Physical therapists focus on exercises that help with balance, postural stability and strength training.
- Occupational & physical therapists will work with families/caregivers to determine the best support and types of modifications a patient will accept.
9. Seek Professional Advice:
- Consult with healthcare professionals, occupational therapists, or geriatric specialists for personalized fall prevention strategies.
- Consider home modifications or assistive devices recommended by professionals.
- Attend educational workshops or support groups to learn from others facing similar challenges.
By implementing these strategies and seeking support from medical professionals who provide preventative medicine, you can ensure your loved ones are staying upright and on their feet. Fall prevention for people with dementia is critical to ensuring your loved one does not experience hospitalization and unnecessary injury. H2 Health helps people with dementia stay upright and healthy through specialized physical, occupational, and speech therapy services in their home. We work on exercises and stretches that prevent falls before they happen. To learn more, call (904) 618-3778 or email seniorservicesfl@h2health.com.
For more resources, check out the Alzheimer’s Association.