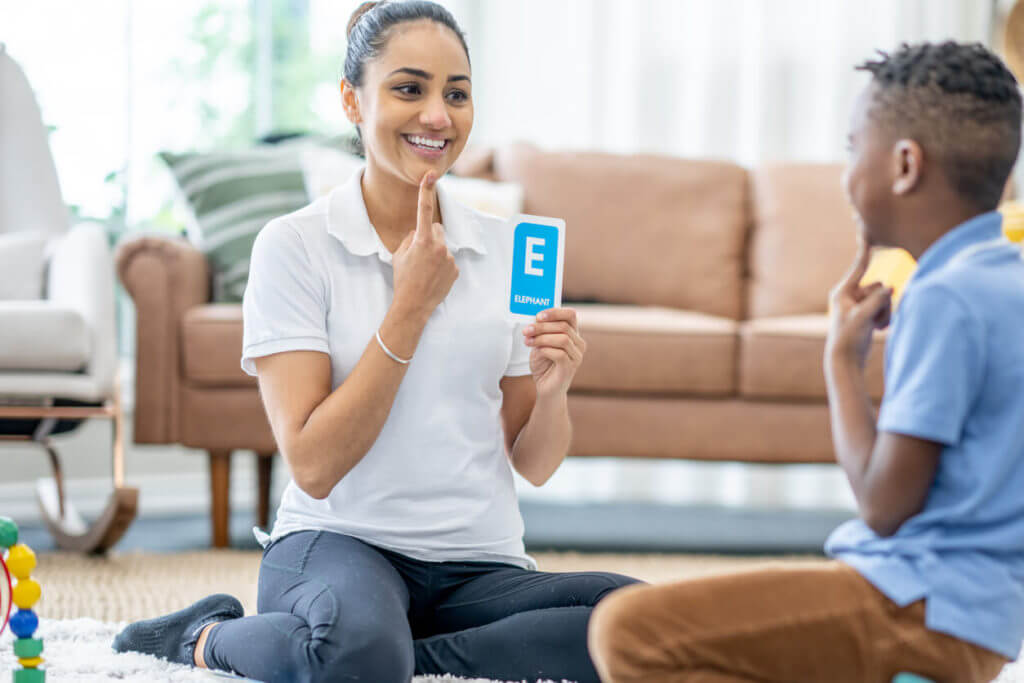
A speech disorder refers to a condition in which a person has a problem creating speech sound that is required to communicate with others, while language disorders refer to a condition in which a person has difficulty with getting their messages across to others and understanding the messages coming from others.
Speech and language disorders can make it challenging for an individual to express their thoughts and feelings to others and maintain their social reputation, affecting their emotional health.
Thankfully, speech and language disorders can be treated. Let’s discuss the common speech and language disorders, their causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
Common Speech Disorders
Articulation Disorders
As the name suggests, articulation disorder refers to the inability to produce specific speech sounds. It is more prevalent in children, especially boys.
Causes: This speech disorder occurs because children fail to coordinate their lips, tongue, teeth, palate, and lungs. Articulation disorder may also have hereditary causes.
Symptoms: People or children with articulation disorder will add sounds or syllables to words that don’t belong there, change a sound that might seem like a lisp, leave certain sounds out of their speech altogether, and substitute one sound for another.
Treatments: To treat articulation disorder, a speech and language therapist recommends speech therapy. They will work with your child and assign them some activities and exercises.
These exercises and activities will help the child identify sounds they cannot make, relearn ways to control the motor parts of the speech, strengthen the muscles involved in the speech, correct the way they create sound, and practice sound formation (at home).
Phonological Disorder
This is a disorder in which children can produce sounds correctly, but they face trouble putting sounds together correctly. For instance, a child may be able to make the sound “d” on its own, but when it comes to saying a word that starts with “d” they replace it with “g”.
Causes: There is no known cause of phonological disorder in children; however, a child is more likely to have a disorder if their close relatives also have a speech problem.
Symptoms: Children do not use some or all of the speech sounds to create words as other children of their age can.
Signs and symptoms of the phonological disorder are that the child either changes or omits the first or last sound of the word; however, they face no problem in pronouncing the same sounds in other words. For instance, they may say “boo” for a book but may have no problem saying “key”.
Treatments: Mild forms of phonological disorder may go away on their own by the time a child reaches the age of 6 years. However, in severe cases, speech therapy is recommended. A speech and language therapist works with your child to help them create the sounds. For example, they may show them where to place the tongue while producing a particular sound and how to form the lips to produce certain sounds.
Disfluency
Disfluency disorder refers to a speech disorder in which there is an interruption in the smooth flow or fluency of speech. Stuttering is the most common disfluency disorder. People with disfluency or stuttering know what they want to say but have trouble saying it.
Causes: Abnormalities in speech motor control and genetics may result in disfluency. In some people, a stroke, traumatic brain injury, or other brain disorder also results in stuttering, a condition known as neurogenic stuttering.
Symptoms: The symptoms of stuttering or disfluency include:
- The repetition of words, sounds, or phrases
- Putting in extra words or sounds
- Making words longer
- Pausing during words or a sentence, often with lips together
- Tension in the sounds or voice
- Hand jerking and eye blinking while talking
Treatments: Stuttering is commonly treated with speech therapy focused on building confidence and enhancing communication skills. A speech and language therapist also counsels patients and their families and provides them with necessary support throughout the speech therapy process.
If needed, a speech and language therapist may also refer the patient to a psychotherapist for cognitive behavioral therapy. Cognitive behavioral therapy will help patients resolve stress, anxiety, and self-esteem problems that lead to disfluency or stuttering.
Voice Disorder
Voice disorder and resonance disorder refer to the change in how the voice of an individual sounds.
Causes: Voice disorders may occur due to digestive conditions such as GERD, cancer of the throat, cleft palate, laryngeal web or cleft, noncancerous growth on vocal cords, and hearing loss. On the other hand, resonance problems result from structural issues such as submucous cleft and cleft palate.
Symptoms: Signs and symptoms of voice disorder and resonance disorder are hoarseness to the voice, inappropriate pitch, discomfort upon voicing, vocal fatigue after talking, etc.
Treatments: Treatments of voice disorders may include laryngeal massage and relaxation, resonance and voice therapy, counseling on vocal health and hygiene, and expiratory muscle strength straining.
Language Disorders
Language disorders are more common in young children, affecting nearly 10 to 15% of children under the age of three years. Children with language disorders experience difficulty expressing themselves to others and understanding what others are saying to them.
Causes: Genetics and nutrition play a key role in problems with language development. Brain injury, damage to the central nervous system, and hearing problems may also contribute to language disorders.
Symptoms: Children with language disorders may overuse “uh” and “um” in their speech because they cannot recall the right word. They also have reduced vocabulary compared to other children of the same age and have limited ability to form sentences and have a conversation with others. They also repeat questions while thinking of the answers and often confuse tenses.
Treatments: Language disorders are treated through collective efforts of speech and language therapists, parents, teachers, and other healthcare professionals. A speech and language therapist offers language therapy, which will be customized according to the child’s unique cause and extent of language problem. A speech and language therapist may also give some useful tips to parents to help with their child’s normal language development at home.
Speech Therapy in Roanoke, VA
If you or someone you love is suffering from speech and language disorders and are looking for highly trained and compassionate speech and language therapists in and around Roanoke, look no further than H2 Health. We have a team of highly trained and experienced therapists who perform a comprehensive assessment to diagnose and treat various speech and language disorders. We offer both adult and pediatric speech therapy at our locations in Salem, Roanoke, Bluefield, Chilhowie, Dublin, Hillsville, Rural Retreat, Tazewell, and Wytheville, VA.
To make a one-on-one consultation with one of our speech-language therapists, call our staff today at (800) 699-9395 or fill out our convenient online appointment request form.