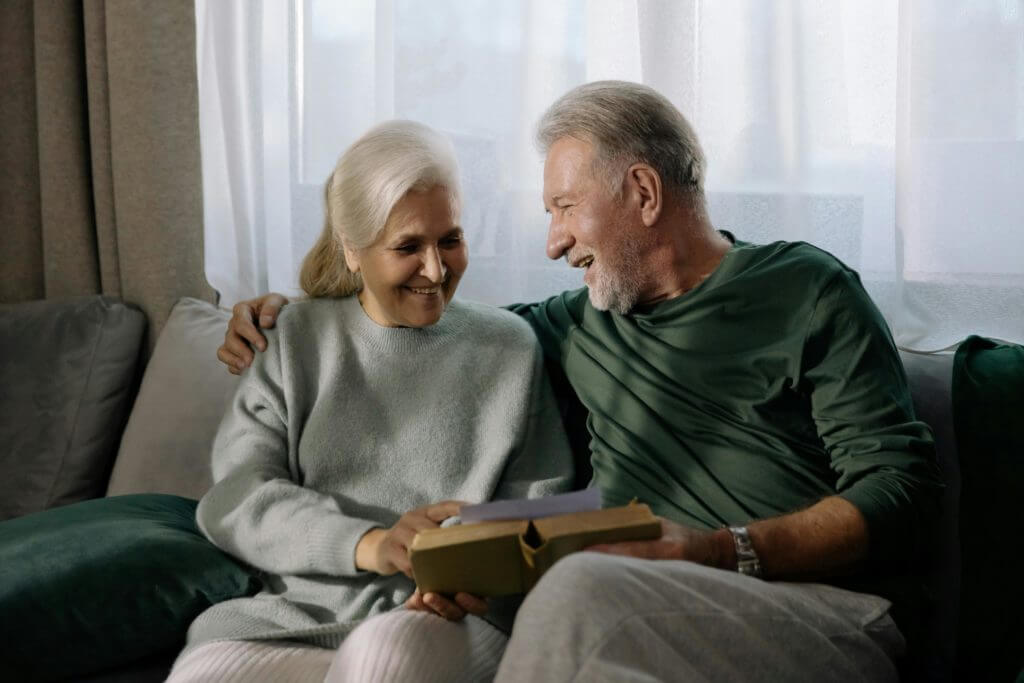
Caring for Caregivers of People with Dementia
Caring for a loved one can be a rewarding experience, but it also comes with challenges, such as caregiver fatigue and guilt. We will explores various solutions and tips to help caregivers overcome these issues. Being a caregiver involves providing support and care for someone with a chronic illness, disability, or other health conditions. While it is a noble role, caregivers often face physical, emotional, and psychological challenges that can lead to fatigue and guilt. This resource guide is dedicated to all caregivers who selflessly provide support and care to their loved ones. It acknowledges the challenges of caregiver fatigue and guilt and aims to provide practical solutions and tips to help caregivers cope with these emotions and prioritize their well-being.
Caregiver fatigue, also known as caregiver burnout, refers to the physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion experienced by caregivers. Sources of fatigue may include the constant demands of caregiving, lack of personal time, inadequate support, and complex medical needs of the care recipient. Caring for the caregiver is essential to ensure the well-being of both the caregiver and the care recipient. By implementing evidence-based solutions and tips, caregivers can overcome fatigue and guilt, fostering a healthier and more sustainable caregiving experience.
Solutions and Tips for Overcoming Fatigue and Guilt
1. Recognize the Signs of Caregiver Fatigue:
• Feeling constantly exhausted, both physically and emotionally.
• Experiencing frequent headaches, body aches, or changes in appetite.
• Difficulty sleeping or sleeping too much.
• Increased irritability, mood swings, or feelings of resentment.
• Neglecting personal needs, hobbies, or social activities.
2. Prioritize Self-Care:
• Schedule regular breaks and make time for yourself.
• Engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
• Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
• Maintain a healthy lifestyle by exercising regularly, eating nutritious meals, and getting enough sleep.
3. Seek and Accept Help:
• Don’t hesitate to ask for assistance from family members, friends, or support groups.
• Delegate specific tasks to others to share the caregiving responsibilities.
• Explore respite care options, allowing you to take temporary breaks or vacations.
• Consult with healthcare professionals or social service agencies for additional support and resources.
4. Set Realistic Expectations:
• Understand that you are doing your best in a challenging role.
• Accept that you cannot do everything and prioritize essential tasks.
• Be flexible and adapt to changing circumstances and needs.
• Celebrate small achievements and recognize your efforts.
5. Connect with Supportive Communities:
• Join caregiver support groups or online forums to connect with others facing similar challenges.
• Share your experiences, concerns, and emotions with trusted friends or family members.
• Attend educational workshops or counseling sessions to gain valuable insights and coping strategies.
• Seek professional therapy or counseling if needed to address feelings of guilt or burnout.
6. Practice Self-Compassion:
• Be kind and gentle with yourself, acknowledging that caregiving is demanding.
• Remind yourself that it’s okay to take care of your own needs and emotions.
• Challenge negative thoughts or self-blame and replace them with positive affirmations.
• Practice self-forgiveness and understand that you’re human and may make mistakes.
7. Utilize Physical Therapy (PT):
• PT can assist caregivers in managing physical strain and fatigue by providing.
• Body Mechanics Training: PT professionals can teach caregivers proper body mechanics and lifting techniques, reducing the risk of injury during caregiving tasks.
• Energy Conservation Techniques: PT can teach caregivers strategies to optimize their energy expenditure while performing daily caregiving activities.
• Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Tailored exercise programs can help caregivers maintain their physical strength and flexibility, reducing the risk of physical fatigue.
8. Utilize Occupational Therapy (OT):
• Occupational therapy can support caregivers in managing daily activities and addressing caregiver fatigue through.
• Task Simplification: OT professionals can help caregivers simplify caregiving tasks, making them more manageable and less physically demanding.
• Adaptive Equipment: OT can recommend and provide caregivers with adaptive equipment that can reduce the physical burden of caregiving tasks.
• Time Management: OT can assist caregivers in organizing their caregiving responsibilities to ensure adequate time for self-care and rest.
9. Celebrate Moments of Joy:
• Focus on the positive moments and small victories throughout your caregiving journey.
• Find joy in meaningful interactions and shared experiences with your loved one.
• Create opportunities for laughter, relaxation, and cherished memories.
• Engage in activities that bring both you and your loved one happiness.
Remember, taking care of yourself is not selfish but essential for providing the best possible care to your loved one. By implementing these strategies and seeking support from others, you can effectively manage caregiver fatigue and guilt, leading to improved well-being and resilience in your caregiving role. H2 Health helps people with dementia live life to the fullest through specialized physical, occupational, and speech therapy services in their home. To learn more, call (904) 618-3778 or email seniorservicesfl@h2health.com.
For more resources, check out caregiver.org